Toward Dynamic Optimization: Combining AI and EBHDL for the Elderly
Honor Award
Research
Guangzhou, Guangdong, China
Haiwei Li;
Zhitong Zhang, Student International ASLA;
Kang Liu;
Wanjing Chen;
Wei Wei;
Xinyi Liu;
Jiehang Xie;
Mi Zhang;
Zhishan Huang;
Min Zhong;
Chuling Cai;
Xixi Huang;
Yongqi Hou, Student International ASLA;
Xiaoling Lin;
Shunyao Yu;
Yan Fang;
Xinyue Feng;
Faculty Advisors:
Chongxian Chen, International ASLA;
Yu Xia;
JIngyi Liu, International ASLA;
South China Agricultural University
This is a very interesting and thought-provoking idea! Well thought out, developed, and tested. It addresses a pressing human environmental concern and the questions of how AI can be applied to help address it. Clear presentation that communicates processes and results.
- 2023 Awards Jury
Project Statement
Therapeutic gardens can provide potential health benefits for the elderly. The Evidence-based Health Design in Landscape Architecture (EBHDL) process model can help deliver stated health outcomes. With the development of artificial intelligence, the growth of computer-aided design can improve the EBHDL process to fill the gaps.
This research project aims to explore how artificial intelligence combined with the EBHDL process model can contribute to the therapeutic garden design for the elderly. The proposed framework was the first attempt to apply different GANs and to determine their applicable characteristics to the therapeutic garden design, making evidence-based health design for the elderly towards dynamic and scientific optimization.
Project Narrative
Background and Objective
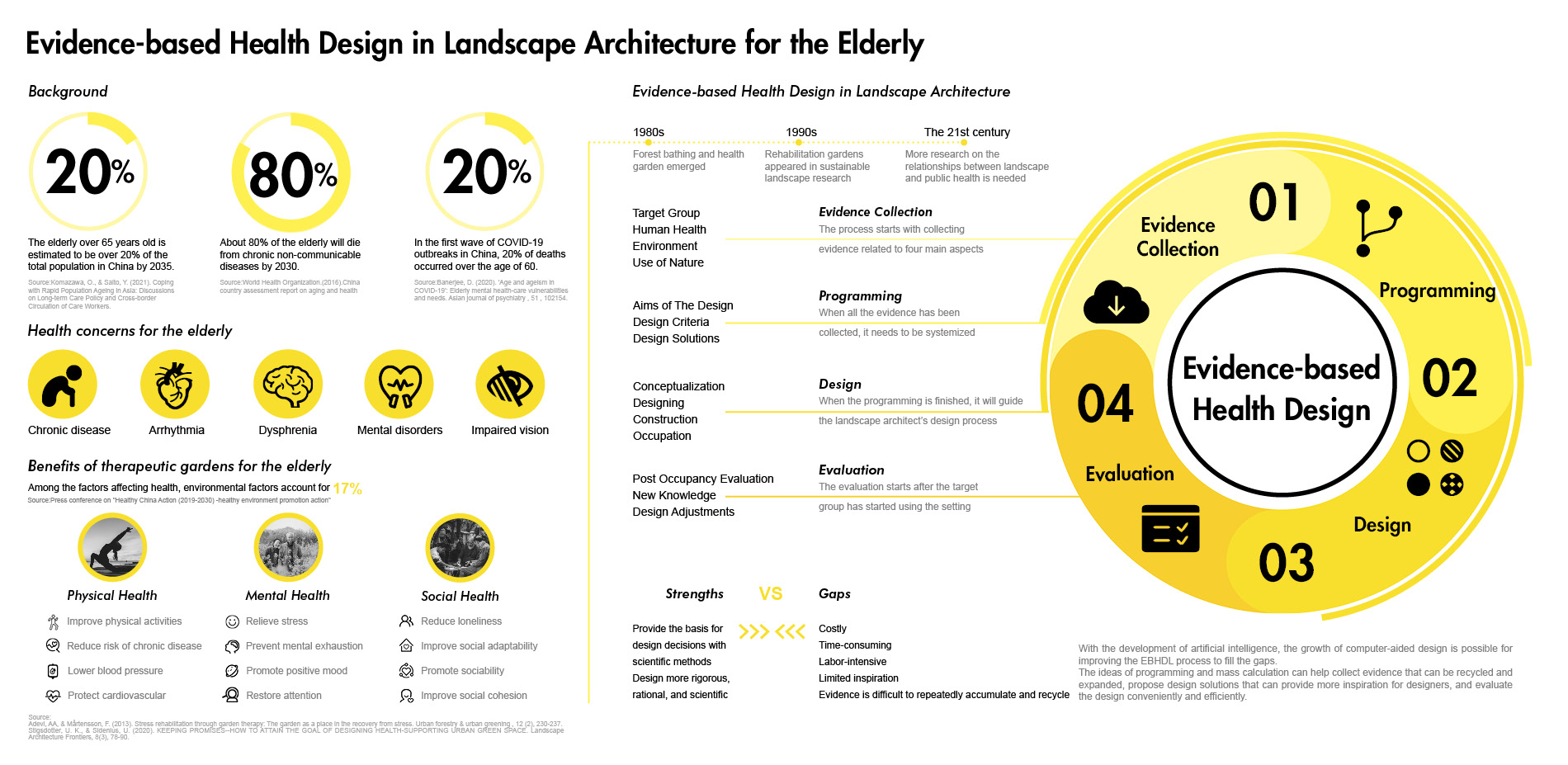
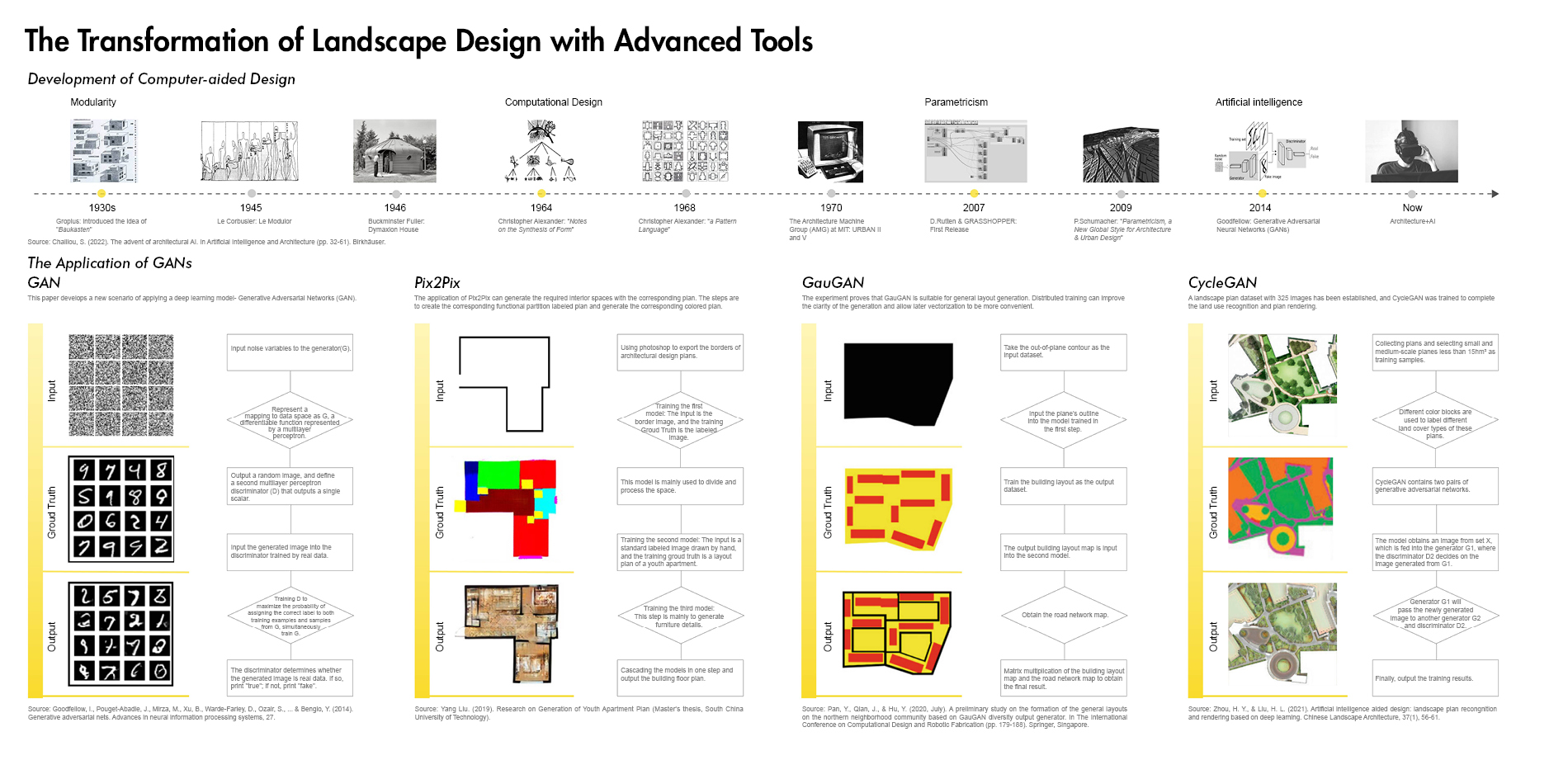
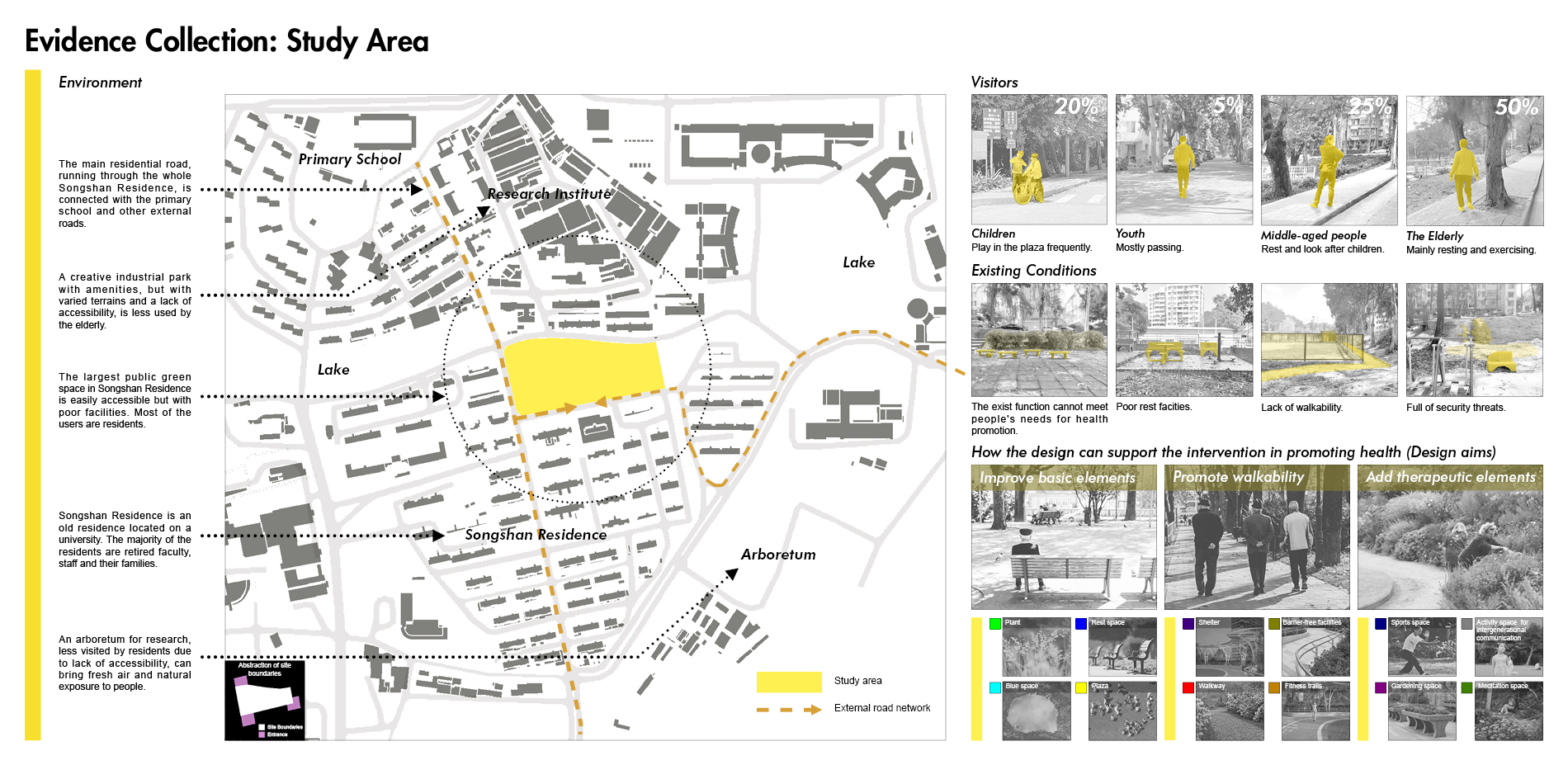
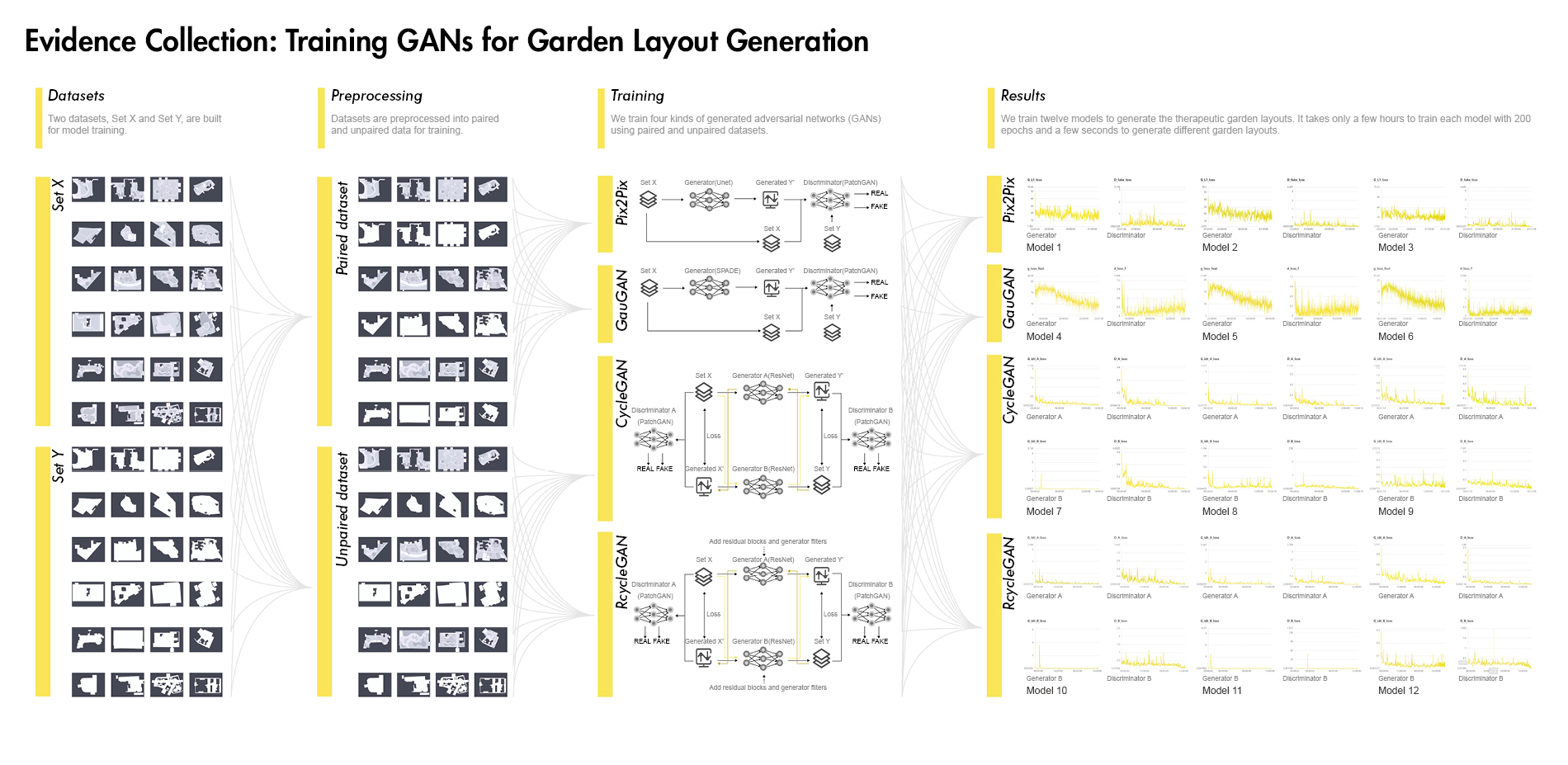
China’s population is aging dramatically, and health issue in old age has become a vital social concern. Providing green spaces, especially therapeutic gardens, is an effective measure to promote various dimensions of health for the elderly by encouraging physical activity, relieving mental fatigue, and facilitating social interaction (Taheri et al., 2021). The Evidence-based Health Design in Landscape Architecture (EBHDL) process model is often considered a scientifically valid approach to deliver on stated health outcomes of therapeutic or healing places (Stigsdotter & Sidenius, 2020). The model provides the basis for design decisions through scientific methods, making the design more rigorous, rational, and scientific. However, the process is a spiral that is time-consuming, labor-intensive, and costly. The growth of artificial intelligence is possible to improve the EBHDL process to create a dynamic and scientific method for therapeutic garden design. Especially the Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), in which ideas of programming and mass can provide more inspiration for designers and evaluate design conveniently and efficiently.
Evidenced-based Health Design for the Elderly
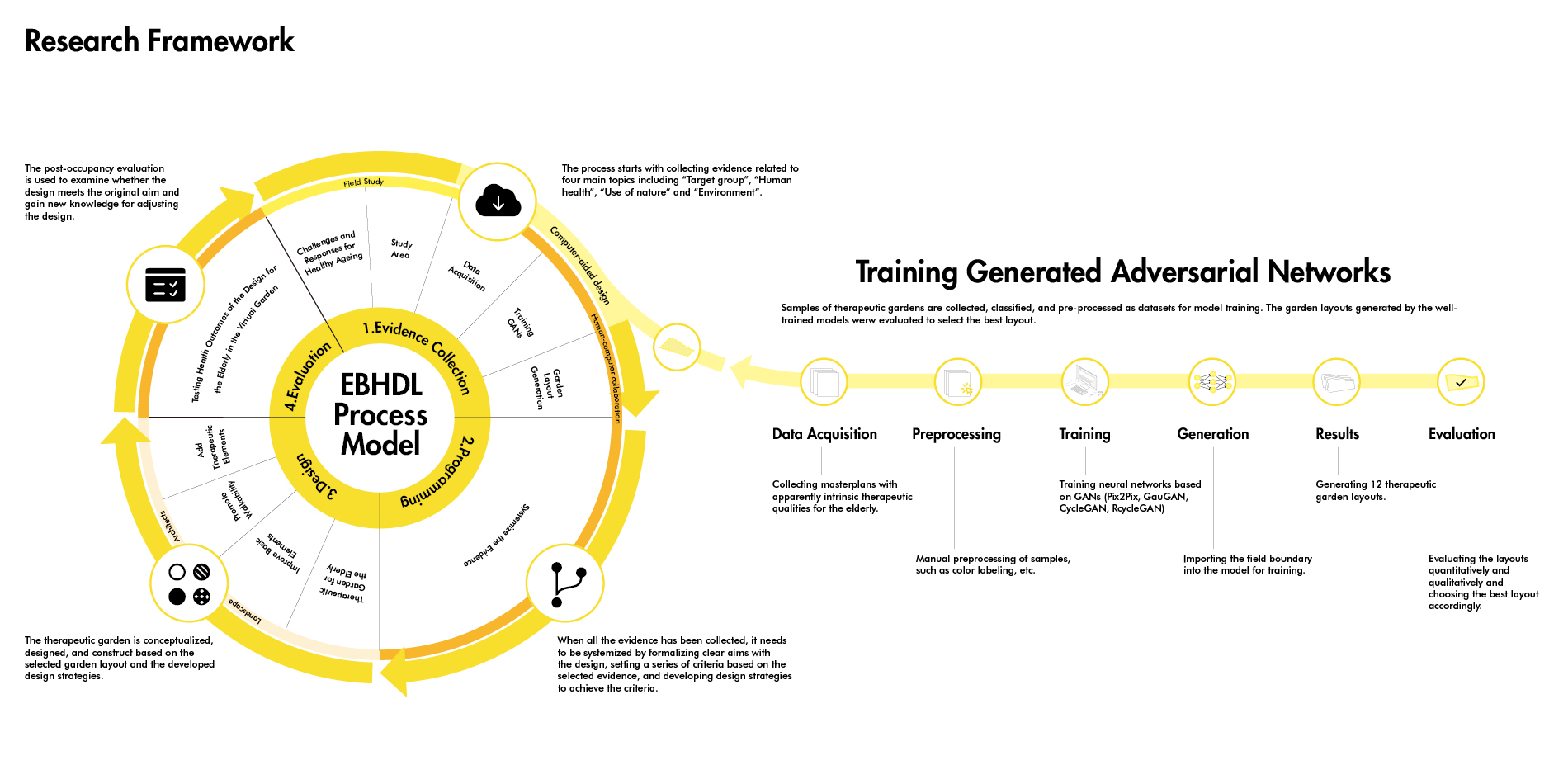
The innovative research framework combines four steps of the EBHDL process model and artificial intelligence algorithms.
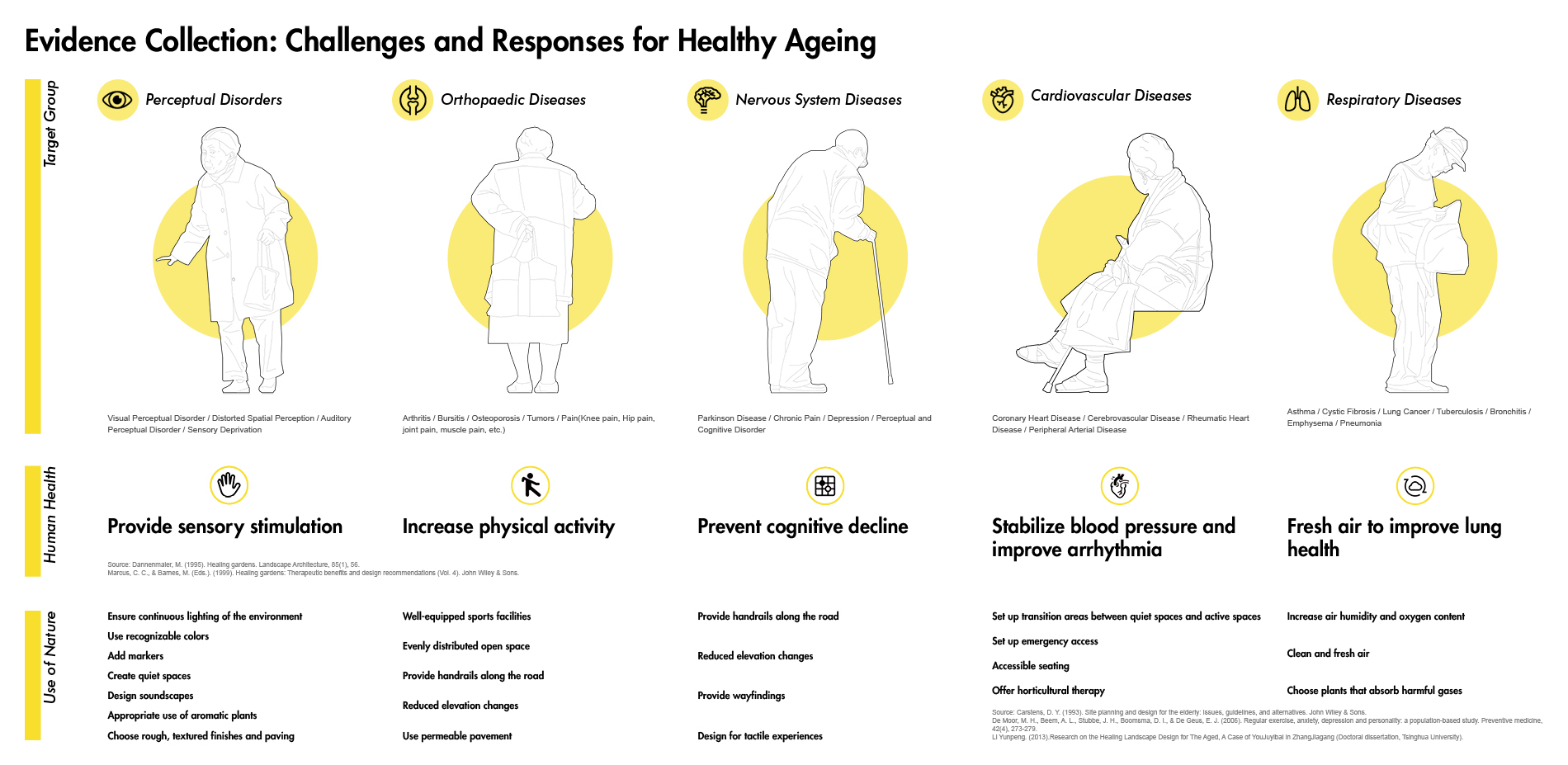
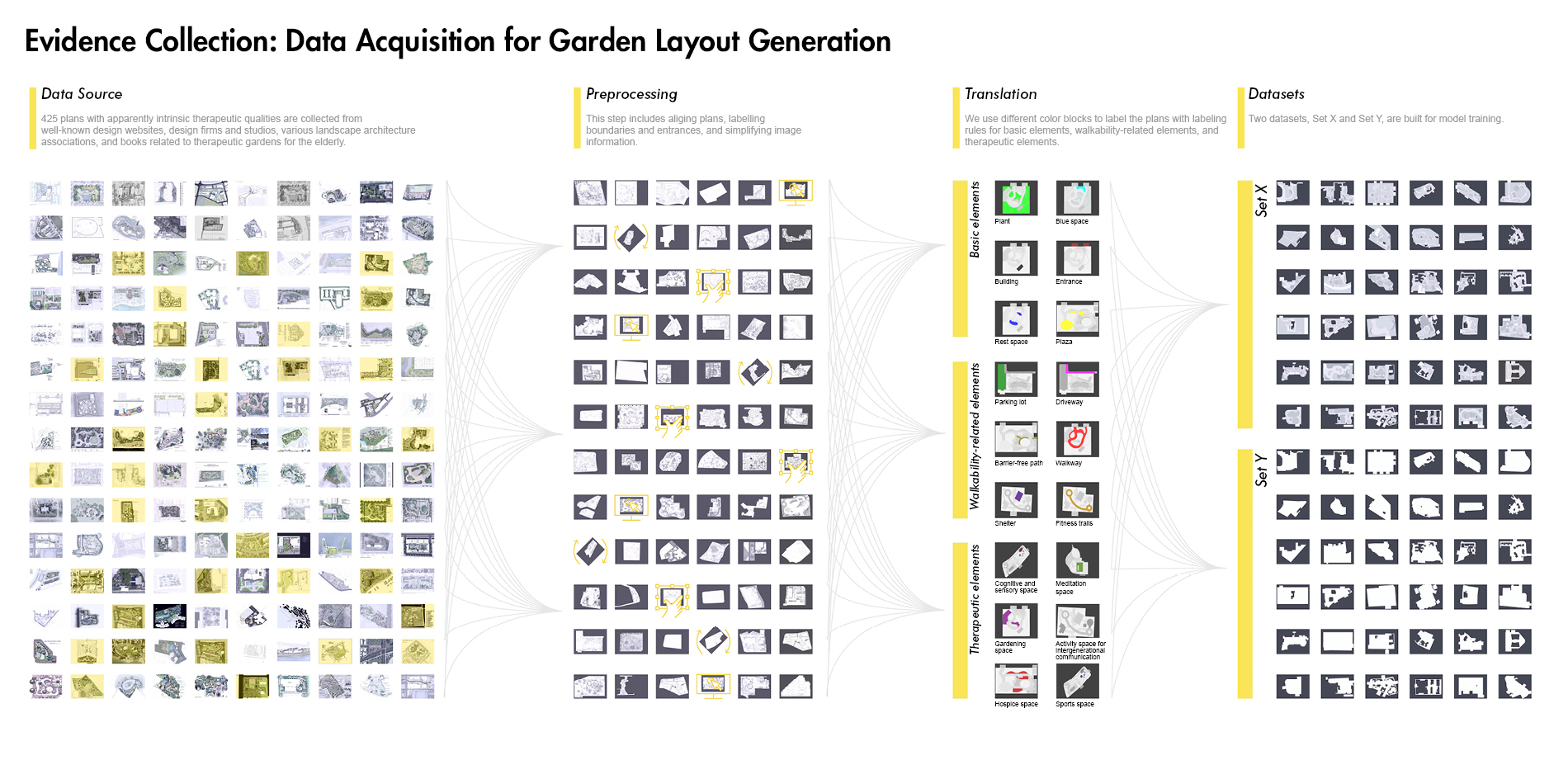
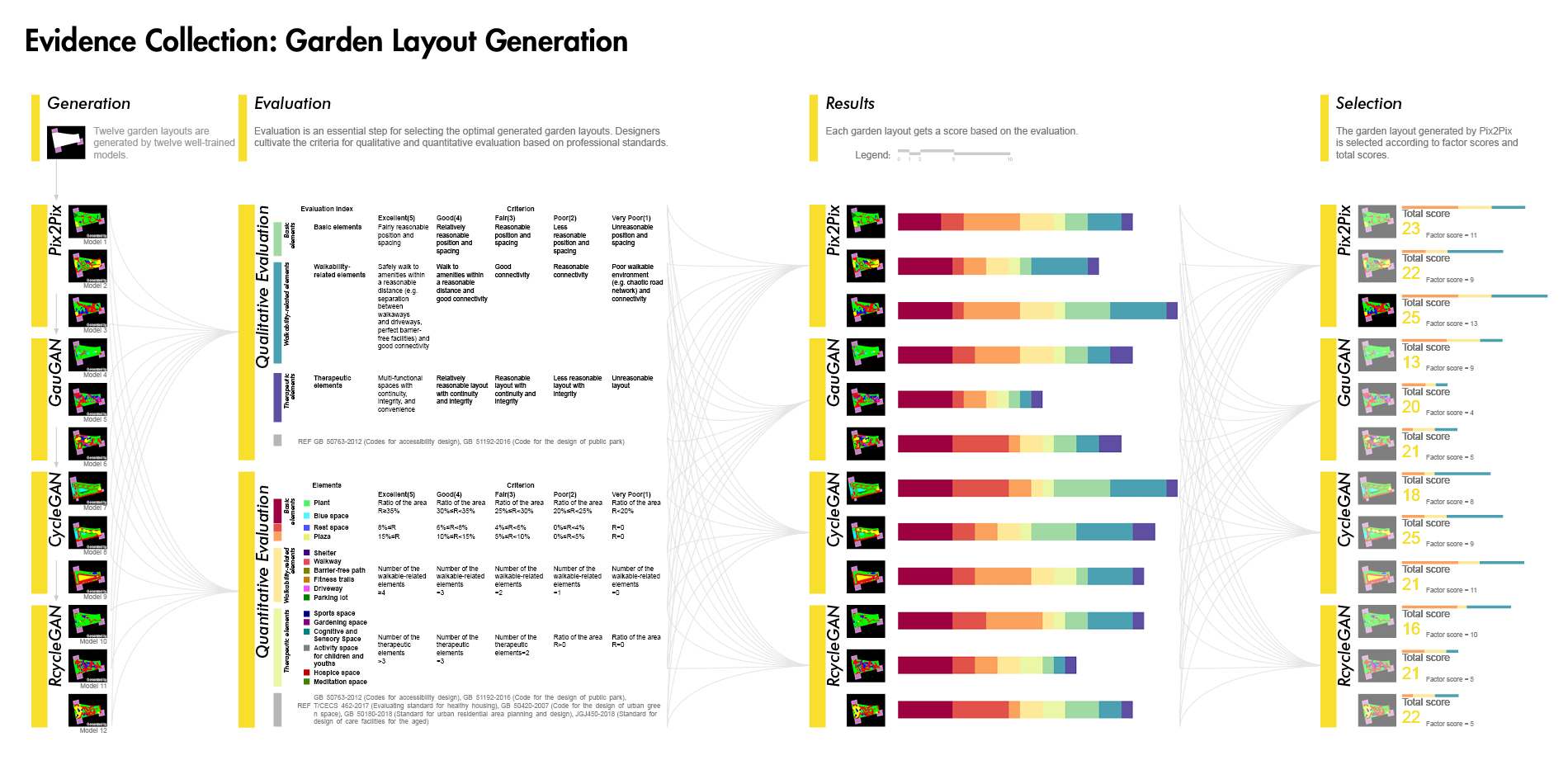
1) Evidence Collection related to healthy aging design with the involvement of artificial intelligence techniques including target group analysis, study area, data acquisition, training neural networks based on GANs, and garden layout generation. To train models generating healthy aging design, two therapeutic garden datasets were built for model training, and then 12 trained GANs models were used to generate garden layouts. To select the best-generated layout, 12 garden layouts are assessed qualitatively and quantitatively by age-friendly environmental criteria.
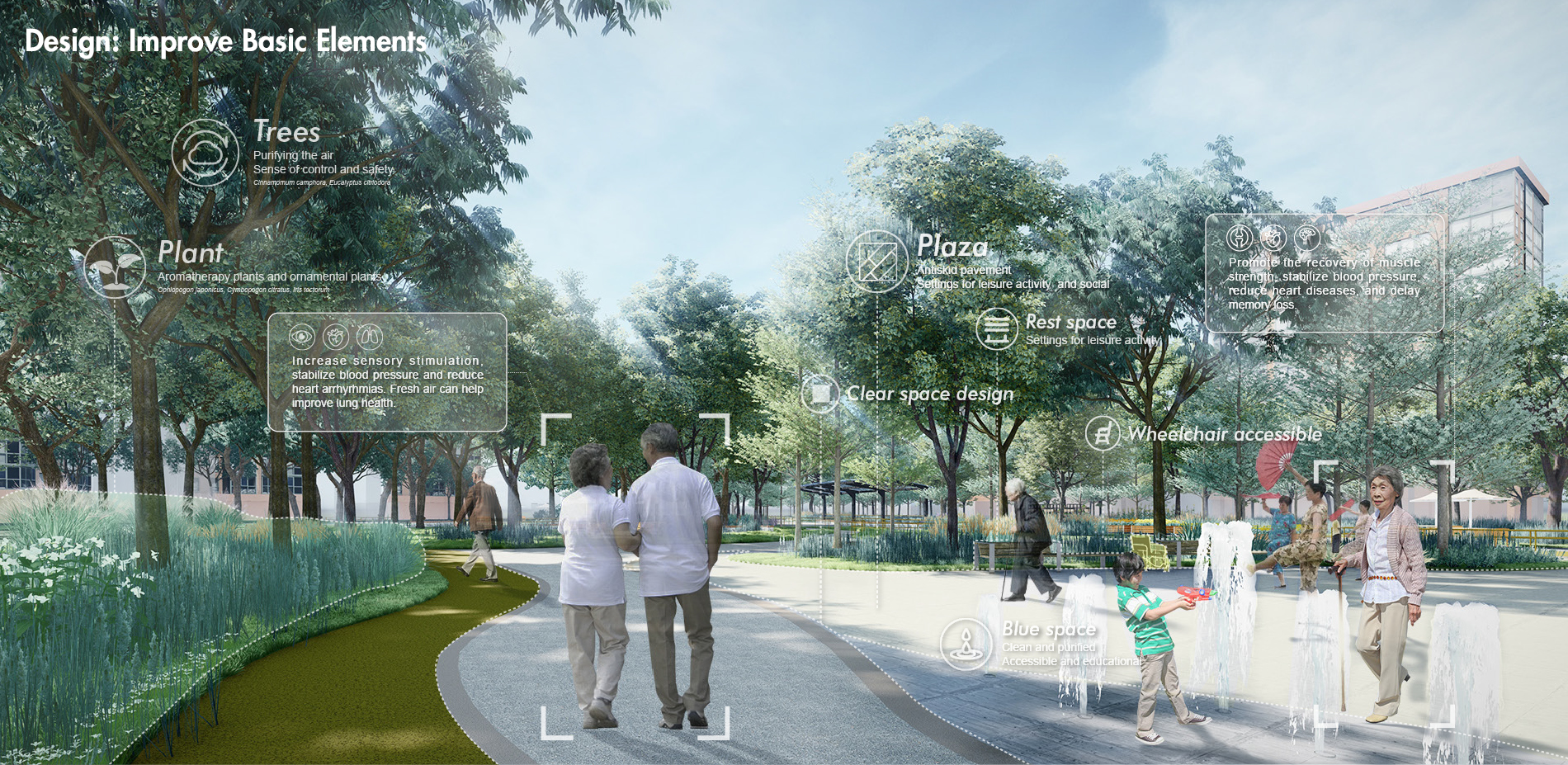
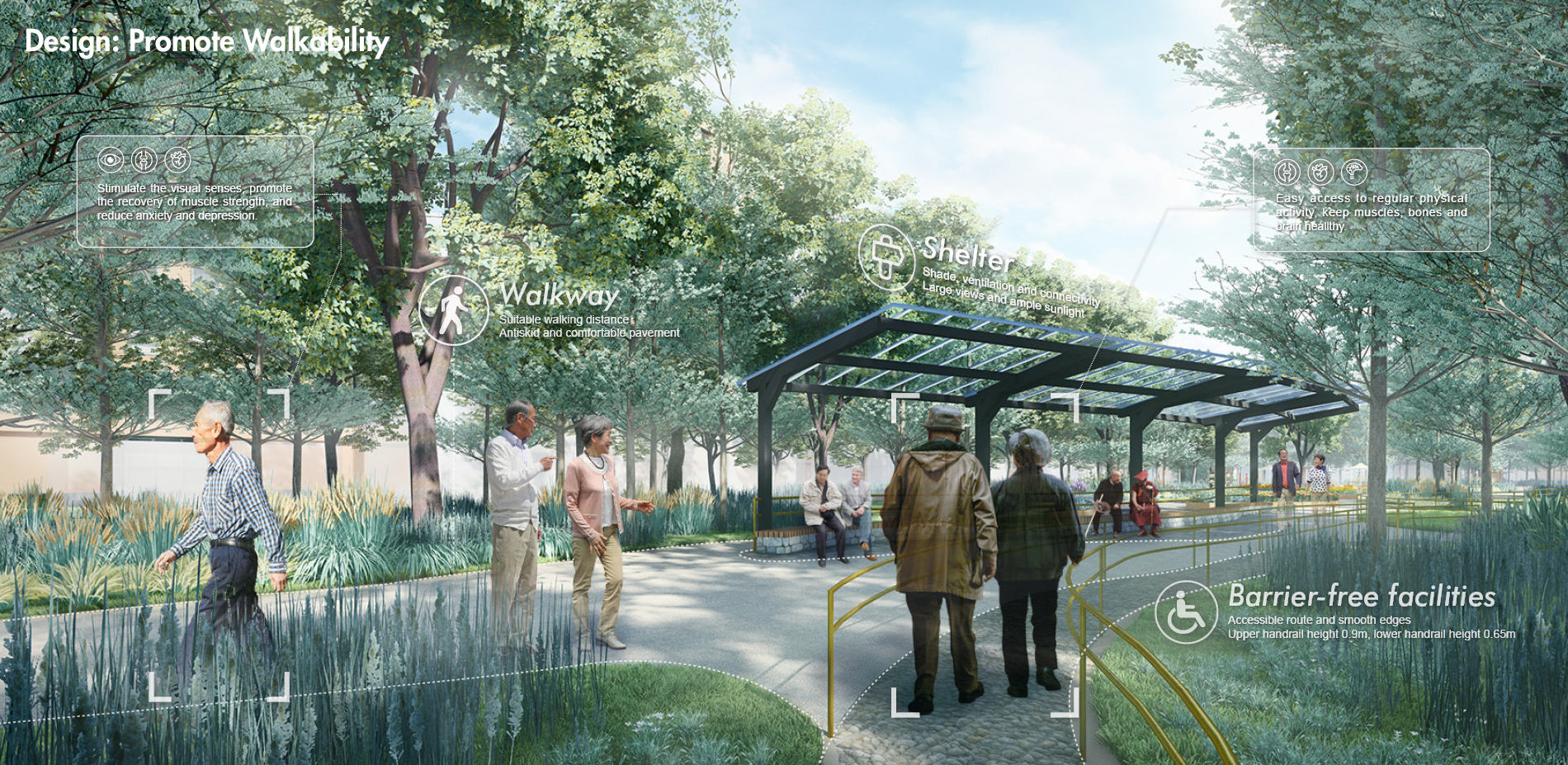
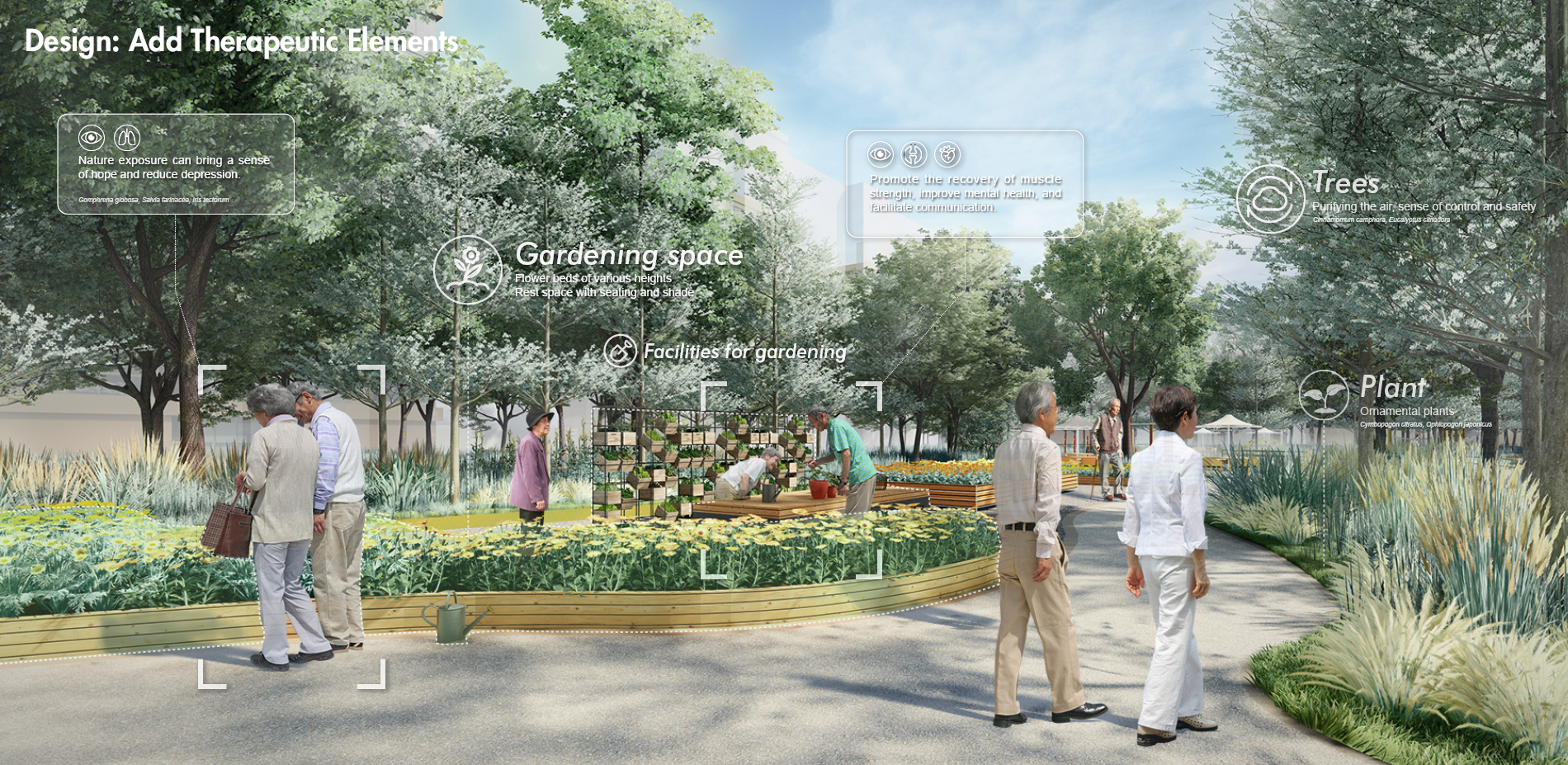
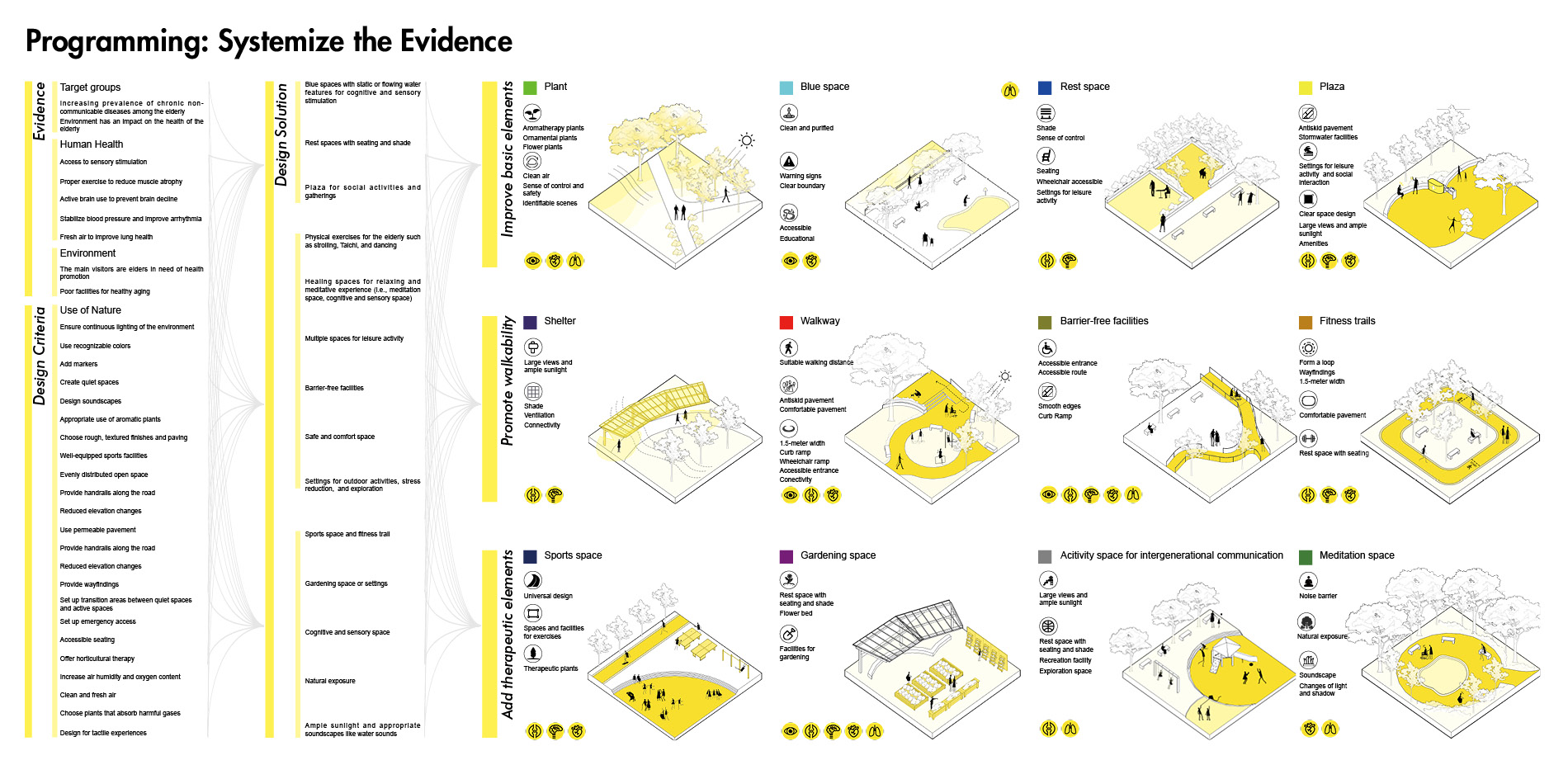
2) Programming. Designers systemize the evidence according to the aims of healthy aging design. Based on the evidence and design criteria, we propose a series of detailed strategies for healthy aging design.
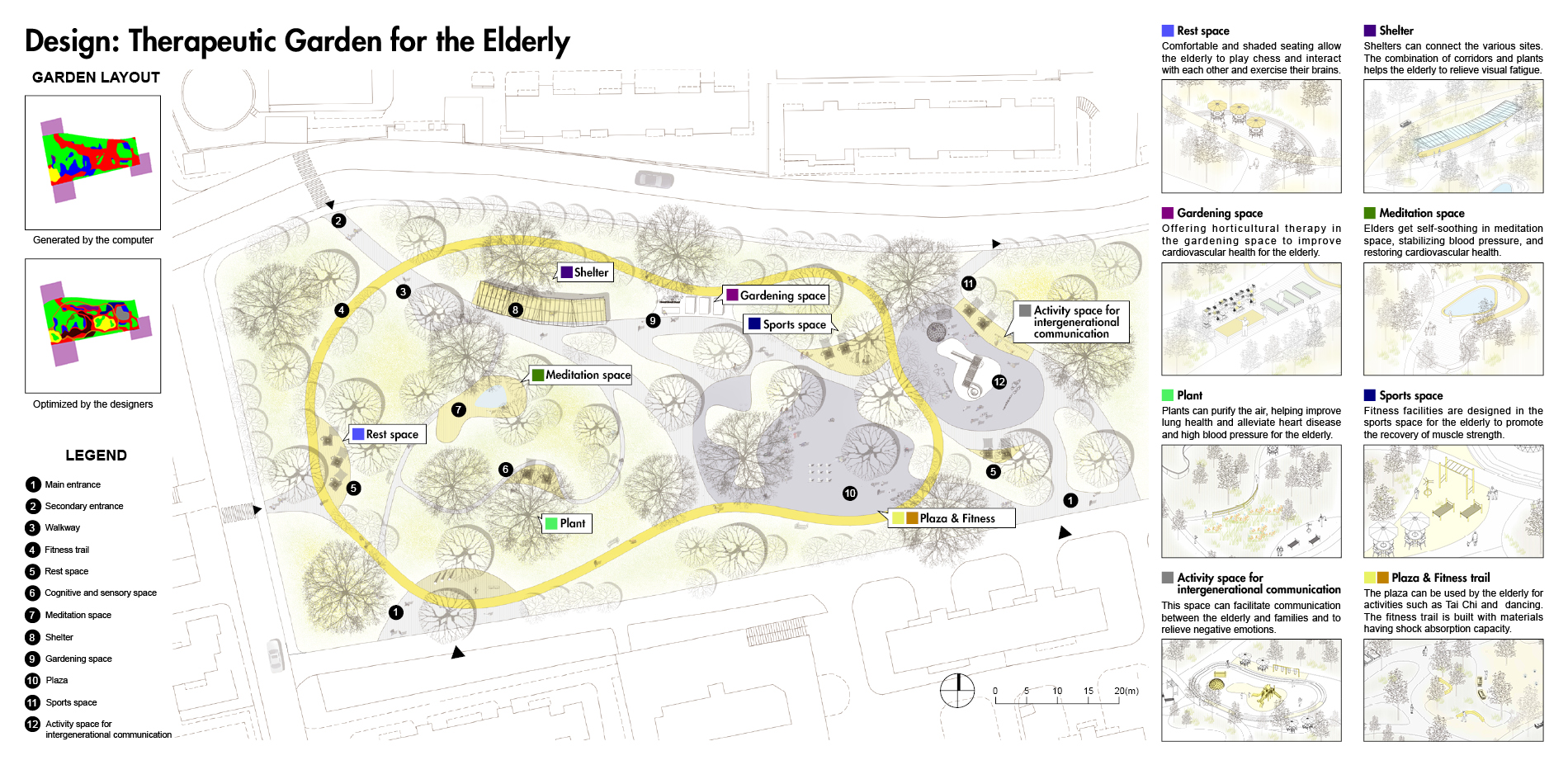
3) Design a Therapeutic Garden for the Elderly. We use the strategies to design and optimize the generated garden layout including basic garden function, walkability-related facilities, and therapeutic opportunities.
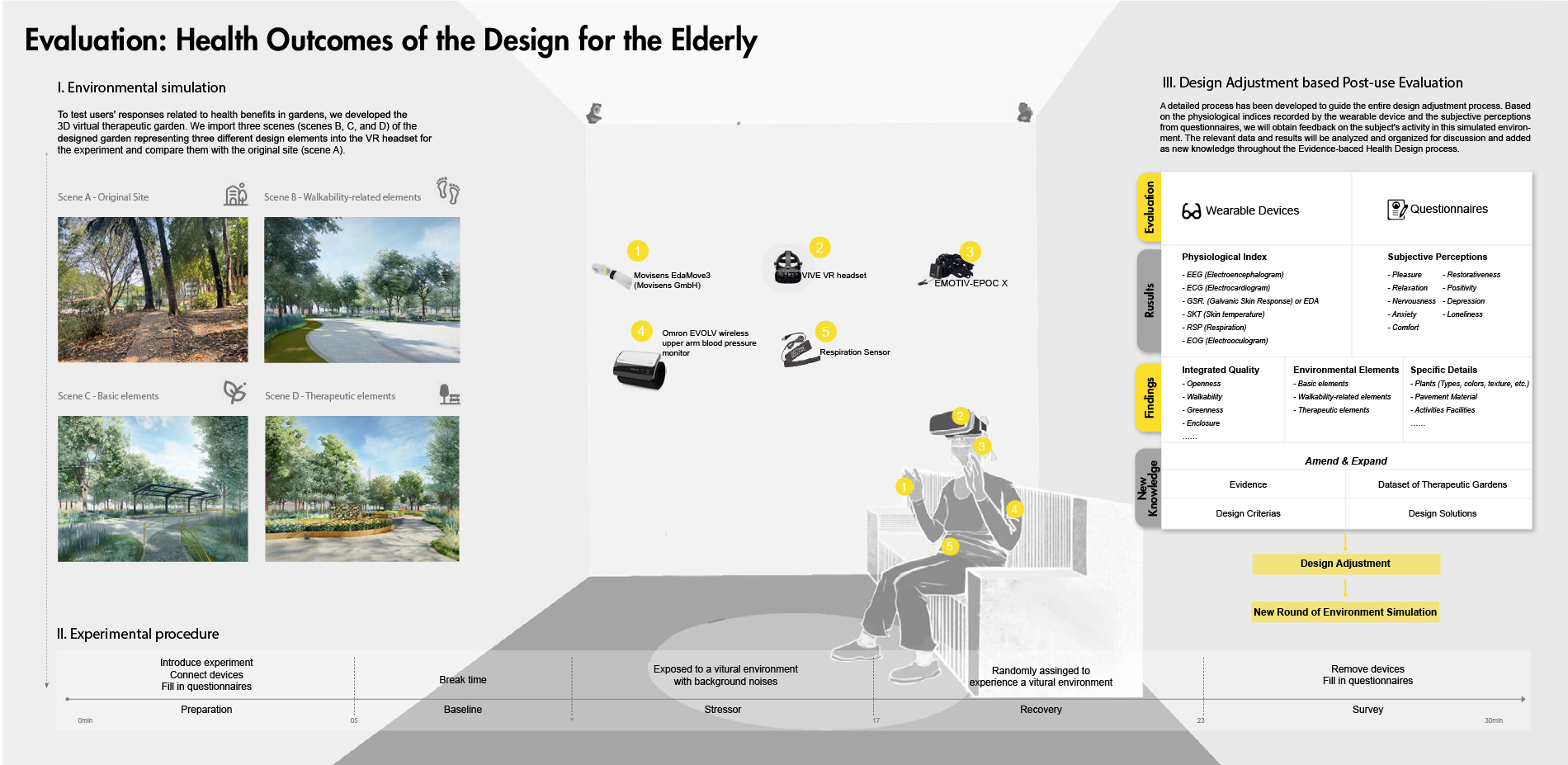
4) Evaluation: Health Outcomes of the Design for the Elderly. We use wearable devices and questionnaires to evaluate elders’ responses related to health benefits in the 3D virtual garden. It indicates that the design can effectively improve the elderly’s health compared to the original site. The new knowledge would be used to adjust the design and push the spiral process of EBHDL.
Significance
This research project has built a framework full of potential and promise, applying advanced artificial intelligence technologies to healthy aging design practices. Humans collaborate with computers based on the EBHDL process model, shifting the design and optimization process toward more objective, scientific, and rational. In summary, this research project effectively develops an interdisciplinary, systematic, and dynamic work process for health design in landscape architecture. Artificial intelligence will soon massively empower landscape architects in evidence-based design practice to be creative, dynamic, and scientific for a healthier environment.
Plant List:
- Broussonetia papyrifera
- Eucalyptus citriodora
- Bombax ceiba
- Cinnamomum camphora
- Magnolia grandiflora
- Acer palmatum
- Ligustrum lucidum
- Osmanthus fragrans
- Camellia japonica
- Pittosporum tobira
- Nandina domestica
- Ophiopogon japonicus
- Gomphrena globose
- Salvia farinacea
- Artemisia argyi
- Cymbopogon citratus
- Iris tectorum
- Lonicera japonica