Honor Award
Remodeling Paradise — Landscape Renovation Round West Lake Region in Hangzhou
Hangzhou, China
Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute,Hangzhou, China, Beijing Forestry University, Beijing and Atelier DYJG, Beijing
Client: Hangzhou Parks and Cultural Relics Bureau
 Close Me!
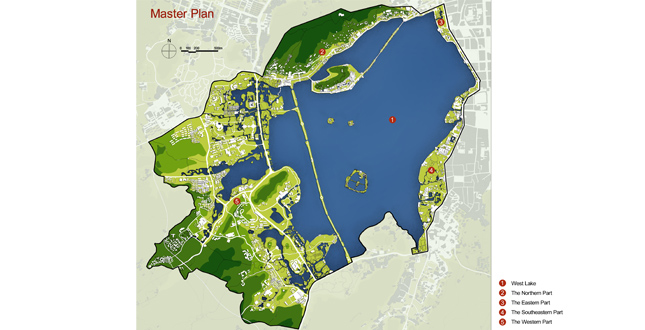
Close Me!Site Plan
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 1 of 16
 Close Me!
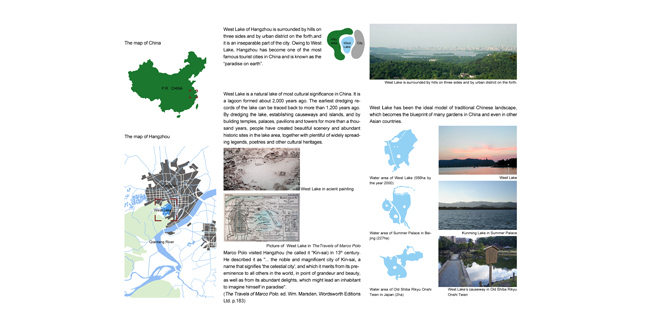
Close Me!Location and History
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 2 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!Background
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 3 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!Complicated Situations to be Dealt With
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 4 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!Analysis and Strategies
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 5 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!The Western Part
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 6 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!The Western Part
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 7 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!The Western Part
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 8 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!The Eastern Part
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 9 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!The Southeastern Part
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 10 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!The Southeastern Part
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 11 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!The Northern Part
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 12 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!Ecological Benefits — water system
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 13 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!Ecological Benefits — vegetation and habitat
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 14 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!Landscape and Tourism Benefits
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 15 of 16
 Close Me!
Close Me!Social Benefits
Download Hi-Res ImagePhoto: Atelier DYJG, Hangzhou Landscape Architecture Design Institute
Photo 16 of 16
Project Statement
In the city of Hangzhou, which is known in China as the "paradise on earth", an extremely complex large-scale landscape renovation project has been planned and completed since 2001. Confronted with multiple challenges, landscape architects proposed different solutions according to the different issues. The implementation of this project has significantly improved the ecoenvironment of this area, stimulated the development of tourism, provided high-quality urban open spaces, and thereby promoted the sustainable development of the city.
Project Narrative
—2010 Professional Awards Jury
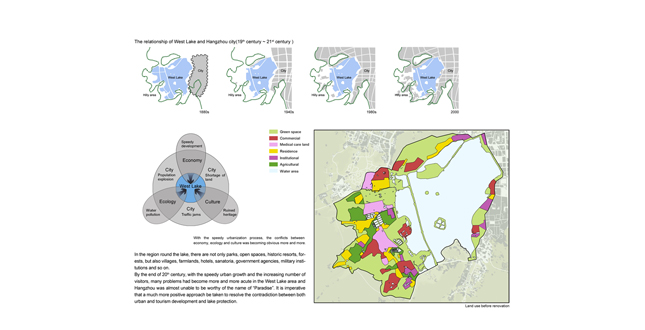
Background
West Lake of Hangzhou is a natural lake of most cultural significance in China. For more than a thousand years, people have created beautiful scenery and plentiful historic sites in the lake area as well as a great deal of widely spreading legends, poetries and other cultural heritages. West Lake has been the ideal model of traditional Chinese landscape and even the model of other Asian countries. Owing to West Lake, Hangzhou is known as the "paradise on earth." By the end of the 20th century, with the speedy urban growth and the increasing number of visitors, many problems had become more and more acute in the West Lake region and Hangzhou was almost unable to be worthy of the name of "Paradise." In view of this situation, the project was proposed in 2001. The local government expected to create a better urban environment, promote the development of tourism, and provide high-quality urban open spaces for citizens by remodeling the West Lake region. The project covers an area of 12.8 square kilometers and almost comprises all significant landscape resources of the city. As it is an extremely complex large-scale systematic project, the landscape architects are confronted with multiple challenges.
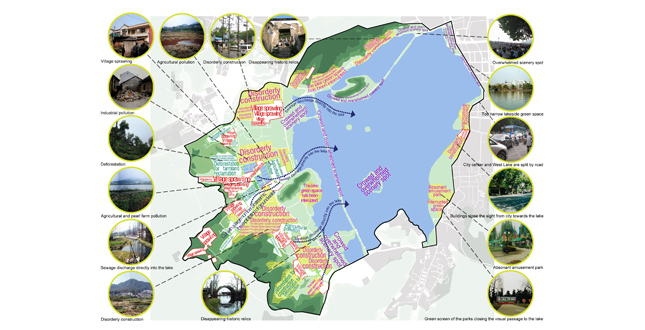
The Complicated Situations to Be Dealt With
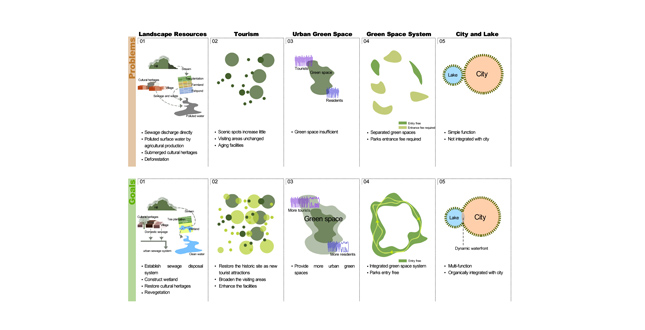
- The urgent need to protect the landscape resources
Natural Resources — Suffered from the serious pollution in the upper reaches, West Lake had been contaminated. Moreover, since the lake did not have powerful self-purification ability, the water quality was inferior. In addition, some unplanned constructions had undermined the harmony of the natural landscape as well.
Cultural Resources — Some well-known tourist attractions were crowded and overwhelmed, and for lack of repairing and maintaining, a number of cultural heritages had been submerged in the clutter settings and faced the risk of disappearing. - The obstacle to tourism development
From the 1950s to the 1990s, West Lake basically remained the number of scenic spots and the amount of visiting areas unchanged, and its facilities were aged and outmoded. At the same time, the rapid improvement of people's living standard and the new national holiday system brought about fast development of tourism. Therefore, the existing conditions became a serious obstacle to the development of tourism industry, an important industry of the city. - The insufficiency of urban green space
Parks around West Lake are the largest and the most important urban green spaces. From 1990 to 2000, the population of the city increased from 1,340,000 to 1,800,000. However, the park area both in the West Lake region and the inner city had increased little during this period of time. As a result, the public green area per capita was becoming smaller. The insufficiency of urban green space brought about a contradiction between civic recreation and tourist visits. - Green spaces remaining to be systematized
As some lakeside places had been occupied by hotels, a sanatorium, local government agencies, military institutions, municipal facilities, the lakeside parks were separated from each other and an integrated system had not been developed yet. In addition, as most of the parks were not free to the public, the pedestrian system along the lakeshore was unable to be connected. - Not being integrated with the city
West Lake used to be a scenic place outside the city. By the end of the 20th century, although the lake adjoined to the city closely, it had not been organically integrated with the city. With a simple function of enjoying scenery and strolling, the lakeside parks lacked vitality and were unable to satisfy the multiple requirements of modern urban open spaces.
As there were different issues to be dealt with according to the locations of each part of the planning area, we proposed different solutions correspondingly.
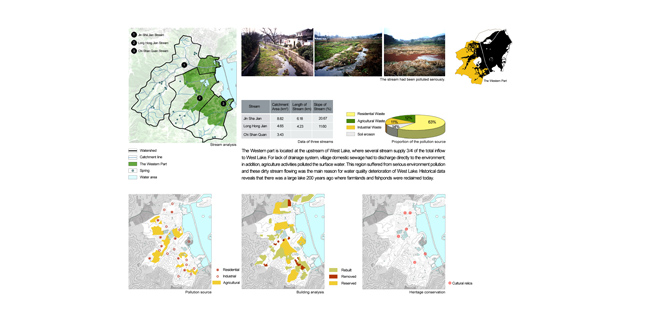
The Western Part
The western part is located at the upstream of West Lake. For lack of a drainage system, village domestic sewage had to discharge directly to the environment; in addition, agriculture activities polluted the surface water. This region suffered from serious environment pollution and these dirty stream flowing was the main reason for water quality deterioration of West Lake. Historical data reveals that there was a large lake 200 years ago where farmlands and fishponds were reclaimed today. Renovation measures are proposed, including: (1) establishing sewage disposal system; (2) transforming most farmlands, fishponds and wastelands into wetlands and woodlands to protect West Lake water source and purify the water; (3) retaining local tea production, the economy backbone of the villages; (4) by means of providing economic compensation and design aids, encouraging the villagers to engage in the tertiary industry through restoring their houses to family teahouses, family hotels or rural restaurants. These measures have greatly improved the ecological environment and increased the area of scenic places in the western part. Some cultural relics and historic sites, which were originally hidden in villages and woods, have attracted a large number of visitors after renovation. Rural teahouses and folk restaurants in beautiful landscape have attracted a large number of residents for relaxation. Both income and living condition of the villagers have been greatly improved.
The Eastern Part
Between West Lake and urban area, the lakeshore originally comprised of a series of linear parks, the average width of which was only 30 meters. In tourist season, the four-meter-wide waterfront walkways were always too crowded to pass by. A busy street separated city's commercial district from the lakeshore. The government decided to put this street underground, thus offering an opportunity to enhance this area. The original street is transformed into a part of the wide waterfront promenade. In this way, the city and West Lake are united as a whole and the lakeshore is more accessible. In addition, in order to transform the urban block into a park, some of the original government office buildings (including the client's own building) on the site have been removed. These measures provide more transition zone between West Lake and the city. Newly-built landscape elements, including grand musical fountain, plazas, water feature, pergolas and pavilions, lighting poles, benches and sitting walls, sculptures, outdoor coffee and tea terrace and so on, make this area become a vibrant and dynamic "urban living room."
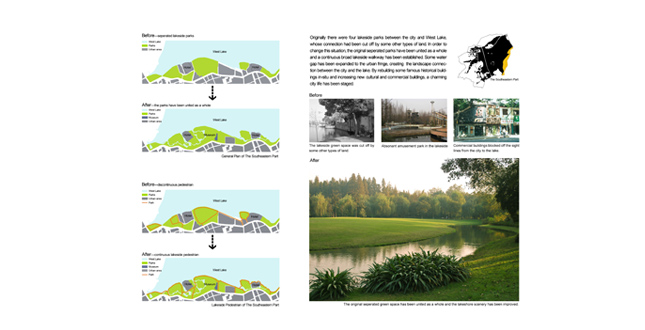
The Southeastern Part
Originally there were four lakeside parks between the city and West Lake, whose connection had been cut off by some other types of land. In order to change this situation, we proposed: (1) through relocating some institutions and transforming the sites into green space, the original separated parks are united as a whole; (2) establishing a continuous broad lakeside walkway; (3) by expanding some water gap to the urban fringe and opening some visual passage to the lake, the landscape connection between the city and the lake is created and the originally green screen of the parks is broken; (4) rebuilding some famous historical buildings in situ, and increasing new cultural and commercial buildings, such as museums, galleries, teahouses, coffees, restaurants and so on, to stage a charming city life.
The Northern Part
The northern part is an area with hills behind and the lake in front. Part of the narrow strip between the lake and city road functioned as a park and part of it as a walkway. In order to transform the lakeside area into a more comfortable urban open space, a number of renovation measures are proposed, including: rearranging vegetation, opening the view lines, building some waterfront platform, widening the walkways and pavement, enhancing the rest facilities. Regarding the foot of hill, the measures include preserving and repairing the historic buildings, demolishing the illegal or low-quality buildings, establishing the view lines and pedestrian links between the hill and lake, thereby improving the tour system of the whole region.
Project Benefits
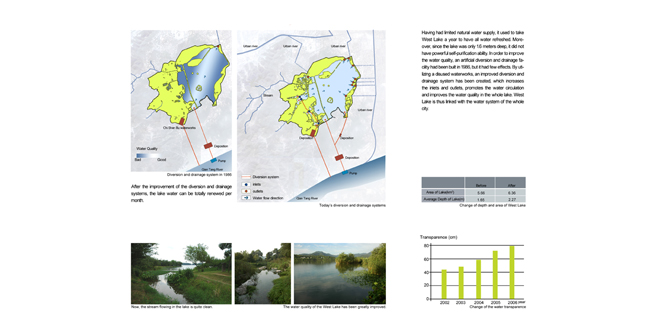
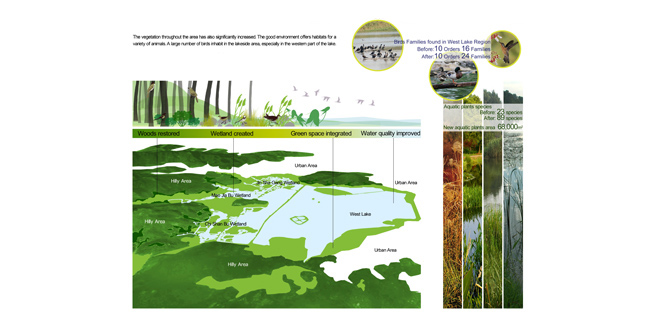
- Ecological Benefits
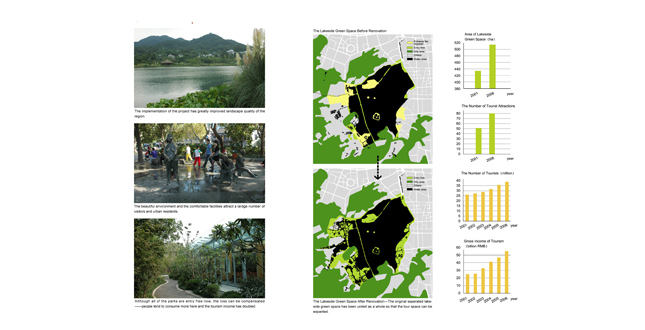
The implementation of the project has significantly improved the ecoenvironment of this area. The pollution treatment and wetlands construction have made the streams limpid before flowing into West Lake. Artificial water diversion and drainage systems have been built and greatly improve the water quality of West Lake. The vegetation throughout the area has also significantly increased. The good environment offers habitats for a variety of animals. - Landscape Value Enhancement and Tourism Development
This project has greatly improved landscape quality of the region. The beautiful environment and the comfortable facilities attract a large number of visitors and urban residents. The number of tourists has increased by 15 million in five years and the tourist income has doubled. - Social Benefits
The project not only concerns about the landscape itself, but also brings about positive effects on different interested groups as well. Improved conditions and preferential policy enable the local villagers embarking on a development harmonious with the environment. The project also has created a large continuous beautiful urban open space with all necessary facilities, which serves both the residents and the visitors properly. According to the survey from 2005 to 2009, Hangzhou has kept the title of "The Best Well-being City in China" for five years. - Comprehensive Benefits
Through this project, the city has greatly enhanced its environment and consequently attracted large numbers of talented people, big companies and capital to arrive. Despite its huge investment, this project is cost-effective in view of the city's accelerated economic growth from its beginning to the present. With beautiful environment, harmonious society and dynamic economy, Hangzhou city once again become an ideal "paradise." This project has become a model of sustainable urban development.
Highlights of This Project
Promoted by a farsighted municipal authority and planned by a team led by landscape architects, this entirely implemented project brought forth far-reaching effects to the city. The problems that the project was confronted with at the beginning were extremely complicated and the challenges were enormous. It's a project of city regeneration more than an urban lake renovation. It's a miracle that the whole task, including planning, designing and construction, was completed in merely six years. It's also a miracle of remodeling the paradise.
Project Resources
Lead Designer
Hangzhou Landscape Architecture
Design Institute
Wei He, Wei Zhou, Minghua Lui
Beijing Forestry University/Atelier DYJG
Xiangrong Wang, Qing Lin
Landscape Architects
Yitian Mao, Hongyan Li, Yong Li, Yonghong Li, Jianzhong Qin, Cunzhi Tong, Hongwei Zhang, Bingyue Han, Jinshi Zhang, Wei Guo, Yongjun Yang, Bin Chen, Ziqiang Zhang, Hongying Bu, Yuechun Lin, Caiping Wei
Client Director
Jianting Zhang
Ecologist
Zhandong Li
Architects
Rong Ge, Zhibin Zhu, Qi Yu, Min Chen
Structural Engineers
Wen Zheng, Xin Gao, Zurong Tao, Guolin Zhou
Hydraulic Engineers
Zhishou Tie, Wei Ye, Dongming Chen
HVAC Engineer
Ye Deng, Junyang Zhou
Electrical Engineer
Rong Zhuo, Guofan Mao
Economic Consultant
Xing Wu